Wall Insulation Materials in The UK – 2024 Guide

- Wall Insulation Materials in The UK – 2024 Guide
- Understanding Different Wall Insulation Types
- Technological Advancements in Wall Insulation
- Choosing the Right Wall Insulation Material
- Installation and Maintenance
- Regulatory Compliance and Building Standards
- Wall Insulation Case Studies
- Insulation Grants in the UK
- Retrofitting Solutions and Challenges
- Environmental Impact and Sustainability
- Maximising Energy Savings with Wall Insulation
- FAQs
In the UK, wall insulation improves energy efficiency and enhances home comfort. It prevents heat loss during winter and reduces heat gain during summer. By forming a thermal barrier, wall insulation helps ensure your living conditions remain comfortable throughout the year.
This guide will help you understand the range of materials available for wall insulation and their specific benefits.
Understanding Different Wall Insulation Types
There are two types of wall insulation available, each with unique characteristics:
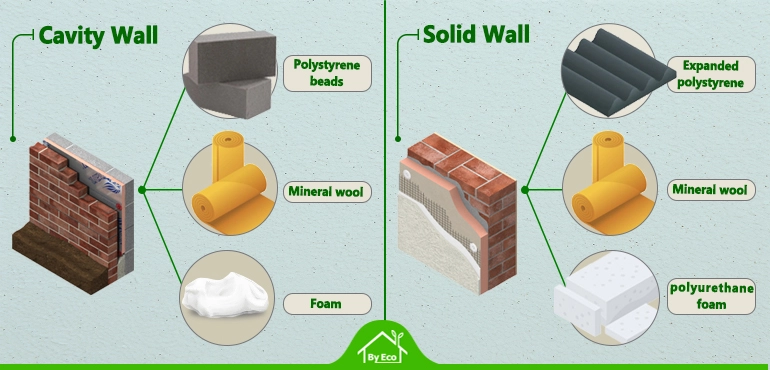
-
Cavity Wall Insulation:
- Materials: Mineral wool, polystyrene beads, or foam.
- Benefits: Effectively fills wall cavities to prevent heat loss. Polystyrene beads and foam offer moisture resistance, while mineral wool provides excellent fire safety and acoustic properties.
-
Solid Wall Insulation:
- Materials: Expanded polystyrene (EPS), mineral wool, or polyurethane foam.
- Benefits: External and internal layers reduce heat loss through solid walls. External insulation offers a fresh exterior finish, while internal insulation provides aesthetic flexibility and enhances internal acoustic comfort.
Technological Advancements in Wall Insulation
Recent technological developments have enabled insulation materials to become more efficient and environmentally friendly:
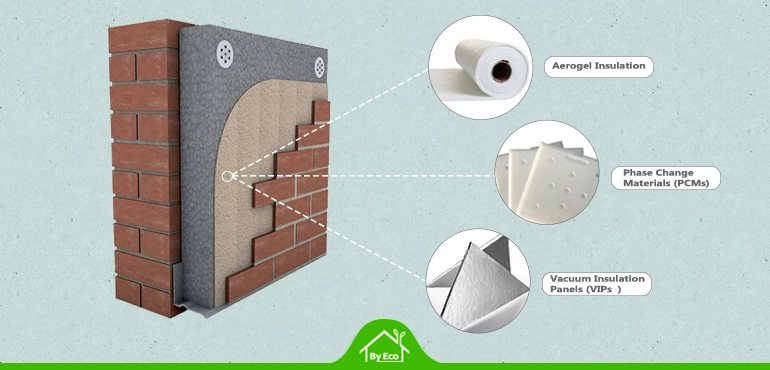
- Aerogel Insulation: An advanced, ultra-light material that provides excellent thermal resistance while being incredibly thin. Ideal for space-limited applications.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels (VIPs): Offer five times the thermal performance of traditional materials. VIPs are suitable for projects requiring maximum energy efficiency with minimal thickness.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): Absorb and release thermal energy, helping maintain indoor temperatures. Ideal for extreme climates or buildings with significant temperature fluctuations.
For the most up-to-date information on our service offerings, including cutting-edge solutions like Aerogel Insulation, Vacuum Insulation Panels (VIPs), and Phase Change Materials (PCMs), you can contact ByEco directly. Our team is ready to assist with the latest advancements in insulation technology tailored to your specific needs.
Choosing the Right Wall Insulation Material
Selecting the right insulation material depends on several factors, including the existing wall condition, aesthetic goals, budget constraints, and specific energy efficiency targets. It’s crucial to consult with insulation professionals to assess which material aligns best with your home’s requirements and your personal preferences.
To aid in your decision-making, the following table provides a comprehensive comparison of common wall insulation materials, detailing their costs, thermal resistance (R-value), moisture resistance, and environmental impacts.
| Insulation Material | Cost (per sq. ft.) | R-Value per Inch | Moisture Resistance | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass Insulation | £0.40 - £1.20 | 2.2 - 2.7 | Moderate | Moderate; mostly recyclable |
| Cellulose Insulation | £0.60 - £1.50 | 3.2 - 3.8 | High | High; made from recycled paper |
| Spray Foam Insulation | £0.50 - £2.00 | 3.5 - 6.5 | High | Low; involves chemicals |
| Mineral Wool Insulation | £0.70 - £1.80 | 3.0 - 3.3 | High | High; often contains natural materials |
| Polystyrene Insulation (EPS) | £0.30 - £0.80 | 3.6 - 4.0 | High | Moderate; recyclable but energy-intensive to produce |
| Polystyrene Insulation (XPS) | £0.50 - £1.50 | 4.5 - 5.0 | Very High | Moderate; recyclable but energy-intensive to produce |
Proper installation is essential to maximise the effectiveness and longevity of wall insulation. This process may vary significantly between cavity wall and solid wall insulation. For cavity walls, it typically involves filling the cavity with insulation material such as foam, beads, or wool. For solid walls, it involves attaching insulation boards to the wall, followed by a protective layer of render or cladding to shield against weather elements and enhance aesthetics.
Ready to upgrade your home's energy efficiency with professional wall insulation? Contact us today to schedule a consultation with our certified insulation experts.
Installation and Maintenance
- Installation: Proper installation is crucial for effective performance. Professional installers ensure insulation panels are securely fixed and appropriately sealed to avoid any thermal bridges or air gaps.
- Maintenance: Conduct regular inspections for wear or moisture buildup and follow up with repairs as needed. Proactive maintenance checks can help extend the life of the insulation and ensure it continues to perform optimally.
Regulatory Compliance and Building Standards
Adhering to local building regulations and standards is crucial for effective wall insulation:
- Building Regulations: In the UK, insulation must comply with Part L (Conservation of Fuel and Power) and Part B (Fire Safety) regulations.
- Certification and Quality Assurance: Use certified products and services, such as those recognized by the British Board of Agrément (BBA).
Wall Insulation Case Studies
To illustrate the practical benefits of different wall insulation types, consider these examples:
Cavity Wall Insulation in Urban Homes:
A terraced house in Birmingham installed cavity wall insulation, resulting in a 30% decrease in energy bills and improved indoor warmth.
Solid Wall Insulation in Period Homes:
A Victorian property in London used external wall insulation to preserve the original interior features. The owners saw a 20% reduction in heating costs.
Insulation Grants in the UK
Investing in wall insulation can be more affordable with the aid of government grants. The UK offers several programs that provide financial assistance for home insulation upgrades, making these improvements more accessible to a wider range of homeowners.
The Great British Insulation Scheme (GBIS)
Launched in April 2023 and running until March 2026, GBIS aims to offer cost-effective insulation solutions to diverse UK households. By supporting the adoption of energy-efficient measures, this scheme significantly enhances access to insulation upgrades, promoting broader implementation across the country.
The Energy Company Obligation (ECO4)
Effective through March 2026, ECO4 concentrates on improving insulation and heating systems within UK homes, with a focus on aiding low-income, fuel-poor, and vulnerable households. This initiative plays a pivotal role in facilitating energy-saving upgrades, including wall insulation, thereby contributing to reduced energy costs, lowered emissions, and enhanced home comfort.
Retrofitting Solutions and Challenges
Older buildings pose unique challenges when retrofitting wall insulation. Consider the following:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the insulation material complements the existing wall structure to prevent moisture accumulation or structural damage.
- Historical Preservation: In listed or historical buildings, opt for internal insulation where external retrofitting could impact aesthetics.
- Access Issues: Difficult-to-reach areas like attic spaces or narrow walls may require specialised installation techniques.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
- Carbon Emissions Reduction: Effective insulation reduces fossil fuel use, thereby lowering carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Materials like wood fibre and certain types of mineral wool are sustainably sourced, promoting eco-friendly building practices.
- Longevity and Waste Reduction: High-quality insulation reduces waste by preventing resource-intensive repairs and replacements.
Maximising Energy Savings with Wall Insulation
Properly installed wall insulation is one of the most effective ways to reduce energy consumption and achieve significant savings on utility bills. To maximise these benefits, consider the following strategies:
Optimise R-Values for Your Climate:
Different regions in the UK have varying climate conditions,
impacting insulation requirements. Aim to meet or exceed the
recommended R-value for your area, ensuring effective heat
retention in the winter and cooling in the summer.
Seal Gaps and Cracks:
Ensure all gaps, cracks, and other sources of drafts in your
walls are sealed before installation. This includes window
frames, door jambs, and any utility pipes. An airtight
building envelope prevents unwanted airflow and increases
the overall efficiency of the insulation.
Combine with Other Insulation Types:
Pair wall insulation with complementary types like loft,
underfloor, or roof insulation to create a more
comprehensive thermal barrier. This holistic approach
minimises heat transfer across the entire building envelope.
Regular Maintenance and Upkeep:
Inspect your insulation annually to identify any damage,
moisture buildup, or pest infestation that might affect its
performance. Repair or replace affected areas promptly to
maintain the insulation's thermal efficiency.
Incorporate Smart Home Technology:
Utilise smart thermostats and energy management systems to
optimise heating and cooling cycles. By fine-tuning indoor
temperatures based on the time of day and room usage, you
can further reduce your energy consumption.
Take Advantage of Government Grants:
Explore government programs like the
Great British Insulation Scheme (GBIS) and
the Energy Company Obligation (ECO4) to
offset insulation costs and achieve a quicker return on
investment.
Professional Assessment:
Consider having a professional energy audit conducted to
assess the current insulation's performance. This assessment
will help identify any areas of weakness and recommend
tailored solutions for further energy savings.
